 Permalink
Permalink Entries in patient engagement (4)
Stanford Health Care Elevates Patient Experience with Design Thinking
 September 5, 2023
September 5, 2023  Navigation Bar for Stanford Health Care Patients“Healthcare today is changing and we need to be a catalyst for change with our patients,” explains Alpa Vyas, Stanford Health Care’s Chief Patient Experience & Operational Performance Officer. “In order to create a superior experience for our patients, we have expanded our understanding of patient needs through empathy, incorporating design thinking into our clinical and operational processes."
Navigation Bar for Stanford Health Care Patients“Healthcare today is changing and we need to be a catalyst for change with our patients,” explains Alpa Vyas, Stanford Health Care’s Chief Patient Experience & Operational Performance Officer. “In order to create a superior experience for our patients, we have expanded our understanding of patient needs through empathy, incorporating design thinking into our clinical and operational processes."
As part of Stanford Medicine, Stanford Health Care has a long history with patient experience and is committed to continuous improvement by collaborating with patients on products, programs and processes. Patient Experience is one of Stanford Health Care’s four main pillars, demonstrating the importance to their organization.
At the PX Symposium in Boston, Alpa will be presenting Design Thinking Rx: A Prescription for Innovative Healthcare Solutions. Join me at the Symposium to learn more about Stanford Health Care and other truly patient- centered organizations. I will be leading a round table discussion to exchange best practices and processes for a superior patient experience.
5 Questions in 5 mins, Interview by Sherri Dorfman, MBA, CEO Stepping Stone Partners
1. How do you define Design Thinking at Stanford Health Care? How does this fit with Human- Centered Design and Co-creation?
“We view Design Thinking as the ‘How’ we problem solve. We start with the end user/patient and use empathy to gain insight into needs to define the problem. Then we move through the Design Thinking process with ideating, prototyping and testing solutions.
We see Human Centered Design as the ‘What,’ our philosophy of engaging with the patient at the center of our process. Co-creation is the ‘Who’. We collaborate internally with our physicians and staff and externally with our patients.”
2. Tell me how Stanford Health Care gathers and leverages insights during the Design Thinking process.
“We use a ‘Collaboration Model’ where we define the problem statement and then refine it with insights collected from internal (e.g. clinical, operational, technical) and external (e.g. patients, family caregivers) stakeholders. We use surveys, discussions and observations. Depending on the project, our internal discussions may point us to others with specific expertise or experience interacting with patients. For patients, we may observe them (with their permission) in the hospital or their home to understand their needs for care and support.”
3. Can you share an example of how Stanford Health Care has successfully used the Design Thinking process to define a better patient experience?
“We are in the process of enhancing the service that our ground navigation team delivers and are excited about what we have discovered. We want to move beyond typical wayfinding services and hospitality approach. Through discussions with our operational leaders interacting with patients who are looking for information and guidance, and via patient surveys and interviews, we learned about the need for improved communication support and better coordination support. We are defining a new, higher level navigation role which will allow us to expand and enhyance our level of patient support. This may include scheduling appointments post discharge from an inpatient unit or emergency department, arranging transportation, securing lodging for family members and providing care updates on for patients – For example, ‘I spoke with the nursing team and they will be bringing you back in 20 minutes’.”
4. Thank you for that specific use case. Tell me how Stanford Health Care is using Design Thinking to address a broader patient problem.
“During the pandemic, we had to pivot on how we provided care ‘Access’ to our patients, from in -person to virtual visits. Looking forward, we want to start thinking about ‘Access’ differently. We are engaging staff and patients in the process of defining the next generation of care, including asynchronous care. We are learning that patients see care ‘Access’ as much more expansive. Based on insights from staff and patients, we are exploring some ideas including PCP eConsults (curbside) with specialists to determine the need and urgency for the appointment and virtual nurse triage.”
5. How does Stanford Health Care measure success for PX initiatives?
“Back in 2022, I contributed to a PX Journal article called ‘Measuring what matters: A proposal for reframing how we evaluate and improve experience in healthcare’. Through extensive discussions with industry experts, the journal article concluded that in order to design experiences that are meaningful, we need to understand what really mattered to patients, families and care partners. At Stanford Health Care, we have looked at our surveys where we ask the same questions and engaged with staff and patients for their feedback. With those insights, we have added questions including those to get feedback on new process enhancements.
We are bringing these survey and discussion insights (including open ended comments) to our operational team members in real- time to translate into immediate changes for our patients.”
With planning underway for 2024, Alpa and her team are interested in further utilizing Design Thinking to develop better programming for Stanford Health Care. “We are working on the next generation of care- exploring ways we can use the insights we have gained to create more personalized experiences for our patients. The Design Thinking process will guide our exploration on how to leverage data and feedback that may be buried within our systems to hone in on specific challenges and solutions – this is where we hope to invest”, Alpa concludes.
 Permalink
Permalink New England Baptist Hospital Hip Replacement- Patient & Caregiver Experience
 June 9, 2021
June 9, 2021  Beginning Surgery ExperienceTwo weeks ago, Sam had hip replacement surgery at New England Baptist Hospital, a top nationally recognized orthopedic facility in Boston.
Beginning Surgery ExperienceTwo weeks ago, Sam had hip replacement surgery at New England Baptist Hospital, a top nationally recognized orthopedic facility in Boston. - Orientation Timing: The virtual meeting was within a few weeks prior, so this gave us ample time to prepare in the days leading up to his surgery date.
- Orientation Content: The hip surgery nurse specialist reviewed pertinent information about what to expect before, during and after the surgery. The follow up emails including “Planning for your Recovery” provided essential information to get Sam’s home ready for his return post-surgery, addressing fall risks.
- Individual Patient & Caregiver Consultation: Since we had some questions that were specific to Sam’s situation, I wish that we had the option to schedule a virtual visit with the nurse to address our concerns in the days leading up to surgery. This would have reduced our anxiety around what to expect Sam to be able to do at different points of recovery.
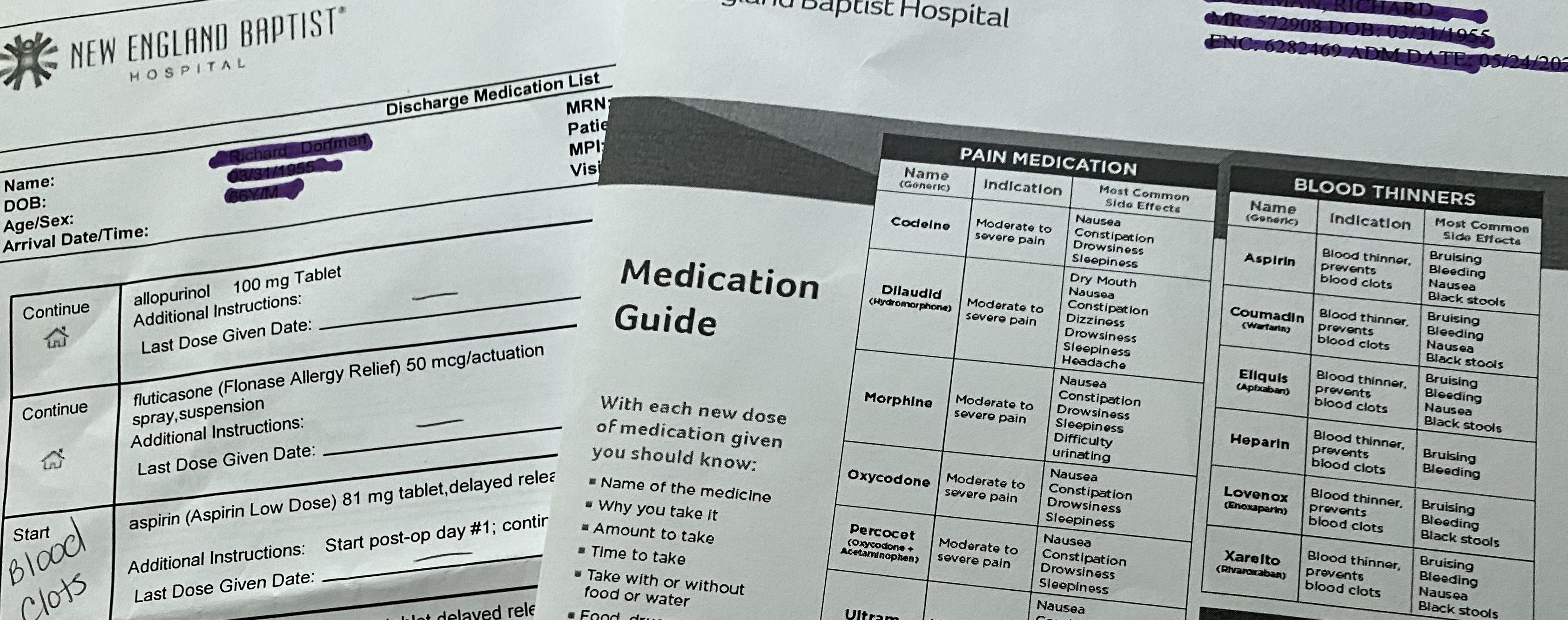 Discharge Medication informationDue to Covid, I dropped Sam off for pre-op with his crutches and cinch sack filled with paperwork and personal items for his stay. Several hours later, I was contacted by his nurse liaison about his status and about coming to his recovery room for a two- hour visit. It was not communicated to me or Sam if he would be staying over or being discharged. As 4pm neared, I asked about his discharge and the nurse moved quickly to get another PT session in to help Sam master stairs. The nurse went carefully through all discharge materials, answered all of our questions and then handed us the folder.
Discharge Medication informationDue to Covid, I dropped Sam off for pre-op with his crutches and cinch sack filled with paperwork and personal items for his stay. Several hours later, I was contacted by his nurse liaison about his status and about coming to his recovery room for a two- hour visit. It was not communicated to me or Sam if he would be staying over or being discharged. As 4pm neared, I asked about his discharge and the nurse moved quickly to get another PT session in to help Sam master stairs. The nurse went carefully through all discharge materials, answered all of our questions and then handed us the folder. - Nurse Liaison: As Sam went through pre-op, he texted me a contact card for the nurse liaison, which gave me reassurance that I had someone to connect with about his surgery status.
- What to Expect Next Discussion: Instead of just telling us what we needed to do at home, the nurse walked us through the folder at discharge, reviewing each patient education insert so we understood what to do and where to go to re-read the information. This took the pressure off of us to remember everything that was mentioned during the discharge meeting.
- What to Expect Packet/Medication: As a caregiver, I was disappointed that there were several different inserts related to medication (Med List, Medication Guide). Although it was quickly mentioned at discharge, it was not documented which medications are to be taken together (i.e. laxative with pain management meds). This would have helped us follow protocol. There also wasn’t a "medication tracking form", so as the caregiver, I had to create my own to record the times that each medication was given and indicate when medications were stopped. There is an opportunity for the provider to gather templates like this from other caregivers and provide them within the discharge packet.
 Post surgery emails tied to surgery date As promised at discharge, Sam received a call from VNA Care to schedule nurse and PT appointments. During these visits, Sam learned how he was doing, what was normal and required a call to the surgeon’s office. These visits have continued over the past few weeks, with the PT providing additional exercises for Sam to do in home.
Post surgery emails tied to surgery date As promised at discharge, Sam received a call from VNA Care to schedule nurse and PT appointments. During these visits, Sam learned how he was doing, what was normal and required a call to the surgeon’s office. These visits have continued over the past few weeks, with the PT providing additional exercises for Sam to do in home. - Care Coordination: Sam felt relieved that his care was continuous and the instructions consistent from the hospital to home, the discharge nurse to VNA Care nurse.
- Recovery perspective: Sam learned from his VNA Care nurse how he was healing relative to other patients. He felt relieved when he was able to master the PT exercises and he was off pain meds “much earlier than other patients” like him.
- Home Health Patient Education and Education Workbook: During the first VNA Care visit, the nurse handed us a 94-page book and pointed out pertinent pages for Sam and for me such as medication categorization and fall preventiion information. This helped us to not feel overwhelmed by the big workbook of information, especailly in the first few days when we are trying to address everything we need to do.
- Patient Education Journey: Sam and I find New England Baptist's post emails informative and relevent since they are tied to his surgery date and recovery milestones.
- Caregiver Post-Surgery Communication: With Sam on pain meds following surgery, it would have been helpful to have all patient communications also pushed to me/caregiver. After he was off of the pain meds and cognizant of what needed to be addressed, Sam forwarded the emails to me. I realized that several would have really been helpful such as what to look for and what to do in the first few days following surgery.
- VNA Visit Alerts: Although the nurse and PT mentioned that they were coming next Monday in the afternoon, it would have been helpful and expected for the patient and caregiver to receive a text reminder with the time range for their visit. Given that Sam is on crutches and often sitting with ice packs on his hip, I need to be available to answer the door for these visits.
- VNA Virtual Visit: As a caregiver, I had questions that needed to be addressed in between the VNA nurse visits. Although I was encouraged to call VNA Care at any time of day or night, I wished that I had the option of a virtual visit to show the nurse Sam’s swelling and bruising. This would have made me feel relieved since the nurse could have seen his hip and leg to make the best care decision instead of relying on my words to convey what I saw.
Oncology Patients experience a personalized journey with interventions and education for better care
 January 15, 2019
January 15, 2019  The National Cancer Institute reports 2017 U.S. cancer care expenditures were $147+ billion, with anticipated increases from our aging population.
The National Cancer Institute reports 2017 U.S. cancer care expenditures were $147+ billion, with anticipated increases from our aging population.
According to Deloitte’s report in Evidence Based Oncology ( The American Journal of Managed Care publication), many organizations are exploring ways to control costs and enhance care quality for oncology patients (e.g. Patient Centered Medical Homes, CMS’ Oncology Care Model).
With many different types of cancer and treatment options, each patient embarks on a personal care journey.
Oncology patients often experience a long journey. Although some steps entail engaging with care staff at a hospital or clinic, most of the time patients are challenged with managing their disease on a daily basis away from the health system.
Healthcare organizations need to closely monitor oncology patients to determine when care and support is required. To be proactive and stay aligned with patient needs, health systems must collect patient information (e.g. Patient Reported Outcomes/PROMs, Patient reported experiences/PREMs). This patient information can guide the care team to intervene, reducing hospitalizations and costs.
Northwestern Medicine’s Oncology Program
“We wanted to take a holistic approach with our oncology patients; mind, body and spirit”, explains Dr. Martha L. Twaddle MD FACP FAAHPM HMDC, Medical Director - Palliative Medicine & Supportive Care, Northwestern Medicine, Lake Forest North Region. “We wanted to help our patients navigate their oncology journey, figure out their new normal and participate in their care”.
“A few years ago, we successfully used a patient engagement care tool with our palliative patients. Our palliative team is embedded within Oncology. Eighteen months ago, we introduced this telehealth type of application to our oncology patients. We felt it would be valuable to extend TapCloud to our general oncology patients because we had seen such a positive response using it for those with high symptom burden and advance disease. We believe many patients and caregivers will benefit from having this tool available to use”.
Patient Experience
How does TapCloud support the oncology patient? What is the patient experience?
 Last month, Robert (not his real name), a 77 year old patient was diagnosed with prostate cancer. Dr. Twaddle and her staff worked closely with Robert through the onboarding process to provide an overview, demonstrate how to use TapCloud, help him download the TapCloud app onto his phone and iPad and discuss what symptoms they will manage to personalize the app for his specific condition.
Last month, Robert (not his real name), a 77 year old patient was diagnosed with prostate cancer. Dr. Twaddle and her staff worked closely with Robert through the onboarding process to provide an overview, demonstrate how to use TapCloud, help him download the TapCloud app onto his phone and iPad and discuss what symptoms they will manage to personalize the app for his specific condition.
The Nurse Coordinator explained “Robert, with this tool (TapCloud), we can think about you when you are not in front of us, get a sense of how you are doing and that we are on the same page”. Robert was relieved to get a message from his Nurse Coordinator confirming that she can see Robert listed on the dashboard to keep a close eye on him.
Most of Dr. Twaddle’s seventy active patients using the TapCloud App are in their 60s and 70s, with a few in their 80s and 90s.
Through the TapCloud app Care Plan, patients like Robert are asked a set of questions. How are you feeling today compared with yesterday? Which of these meds are you taking? Which symptoms are you experiencing today? Symptoms that were selected the prior day are displayed bold. Patients can add symptom(s) which typically takes less than a minute to provide this critical information.
Symptom tracking is made easy by using a word cloud. Each day, the patient sees a personalized word cloud containing symptoms. This personalized symptom cloud incorporates his condition and medications and his list is continuously enhanced from machine learning. TapCloud’s predictive symptoms cover 100+ conditions and 14,000+ side effects. The patient simply touches those symptoms he is noticing. Additionally, he views personalized education based on his journey stage (e.g. tips for managing chemo side effects) and what he is experiencing. He can also upload this biometric information (e.g. vitals, etc.).
How has Northwestern Medicine used the TapCloud tool to deliver better care to Oncology Patients?
 Dashboard displays demo data only
Dashboard displays demo data only
- Prioritize Patient Outreach. The TapCloud platform analyzes all the patient clinical and self- reported data in real time. Using advanced algorithms, patients with a clinical need are identified and alerts are sent to the care team. Patients are prioritized based on alerts, severity and risk. Nurses use the TapCloud Triage Dashboard to efficiently track, monitor and respond to patients requiring an intervention. Nurses can drill down on a specific patient to see how many days since check in, recent events (e.g. vitals, medication usage), pain and anxiety levels.
- Intervene on specific symptoms: Instead of “fishing” for information about how a patient is feeling or having the patient end up in the ER, Nurse Terri can call the patient and say “I've noticed that you've had increased pain the past 2 days…”. TapCloud can also be set up to send alerts for symptoms associated with a patient’s treatment. Patients can send a picture within the TapCloud app with a secure message about their concern.
- In the Patient’s Words: “We had one patient who didn’t feel pain but entered ‘yuk’. He selected that to communicate in his words what he was feeling. One of the features that I really like is journaling. A patient may share that today he is ‘discouraged by his illness’. Although he does not expect us to respond, it gives us insight into how he is doing and the support that he may need from us”, shares Dr. Twaddle.
- Stay Connected with patients who do not come in regularly: When patients are going through infusion treatment, Dr. Twaddle explained that her team sees them on a frequent basis. “However, when our patients are on oral chemo, we feel that TapCloud is especially valuable to give us a window into their experience. We risk losing them because they cannot tolerate the medications and stop without communicating to us.”
- Address Patient Needs with Right Resource: When patients are not in the Clinic or Hospital, it is important to understand what they need. “We may see in a patient’s journaling that she is feeling afraid which is not physical but may be best addressed through our psych- social resource. Or a patient may be ‘running out of her medication’ or ‘checking in on an upcoming appointment’, which can be managed by our Nurse Coordinator."
Measuring Success
Dr. Twaddle uses a set of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the success for the TapCloud solution for oncology patients including:
1) Patient Engagement. How involved are patients in participating in their care? How often did they check in with the app? Which symptoms are most common? What are the new symptoms that have been added by the patient?
2) Improved symptom management. Was pain successfully controlled (e.g. pain scores, pain direction)? Were negative symptoms (e.g. fatigue, bloated, shoulder pain) managed in a timely and effective manner?
3) Cost reduction. How much money was saved by avoiding ER through interventions on symptoms? “When one of our cancer patient ends up in the ER, we explain that we may be able to help avoid the admission with a check in on the TapCloud tool. We had one patient with a side effect that we could have spotted and intervened since it was dangerous for her”.
“We have found that TapCloud is helpful both with cancer patients who have declining function (e.g. pancreatic, advanced lung, brain tumor) and with those that may be curable (e.g. head & neck, breast)", shares Dr. Twaddle.
AMITA Health’s Program will leverage TapCloud
AMITA Health, one of Illinois’s largest health systems is in the process of planning their program which will use TapCloud.
“When I first heard about TapCloud, I was on board immediately”, explains Dr. Robert O. Maganini, Breast Cancer Specialist at AMITA Health. “We have a compliance problem with our breast cancer patients. Although the hormone therapy treatment (e.g. Tamoxifen, Class Aromatase inhibitor) is for five years, some patients will stop after two years because of the side effects. Our working theory is if we have insights into where these patients struggle and when, we can do more aggressive interventions instead of waiting for their next appointment”.
“Our plan is to offer TapCloud to all 200 patients who want to use it, from newly diagnosed to those in year two when we experience a drop in treatment adherence”. After describing his patient population – mostly women 40-75 years old, Dr. Maganini expects a high opt- in rate since it is “ideal for them because it enables faster and more convenient access to their provider”.
Like Dr. Twaddle, Dr. Maganini is planning to use a patient- centric approach when introducing TapCloud, ensuring that patients understand why they are using TapCloud, how to use it, and when to use it.
Dr. Maganini plans to introduce TapCloud to patients at the time of diagnosis. Nurses (e.g. NPs, Navigators) will get patients set up and show them how to use the digital health application. “Since surgery is typically the first step, we plan to use as a follow up with discharge instructions. For those in going through chemo treatments, we will monitor their symptoms. We want to get our patients accustomed to using TapCloud and then they will be using it for the long run with hormone therapy”.
As part of the planning process, Dr. Maganini is working with his team to define the list of side effects including the words that these patients use to describe them. He is leveraging his own and his nursing staff’s patient experiences to devise the TapCloud symptom list in “patient speak”. This is helpful to patients who often struggle to describe their symptoms and feelings.
From this program, Dr. Managini expects to learn about the top side effects, interventions and the effectiveness of the interventions. He will be looking at different success factors – “increase in the therapy completion (3, 4, 5 years) and longer term (beyond the 2 years) hopefully a decrease in mortality rate and reoccurrence”.
“With a program showing demonstrative effectiveness, we envision scaling this to the AMITA Health 2.0, 19 hospitals”, concludes Dr. Managini.
 Permalink
Permalink  consumer generated health and wellness content,
consumer generated health and wellness content,  mobile health and wellness texting,
mobile health and wellness texting,  patient education,
patient education,  patient engagement,
patient engagement,  patient experience,
patient experience,  patient journey,
patient journey,  patient reported experience measures,
patient reported experience measures,  patient reported outcome measures,
patient reported outcome measures,  personalization for health and wellness in
personalization for health and wellness in  AI consumer engagement,
AI consumer engagement,  Behavior Change Health & Wellness,
Behavior Change Health & Wellness,  Care collaboration,
Care collaboration,  Caregiver digital health,
Caregiver digital health,  Connected Health,
Connected Health,  Data Driven Health Engagement,
Data Driven Health Engagement,  Decision Support eHealth,
Decision Support eHealth,  Patient Decision Support,
Patient Decision Support,  Patient Engagement,
Patient Engagement,  Personalization eHealth,
Personalization eHealth,  Population Health,
Population Health,  TeleHealth,
TeleHealth,  TeleMedicine,
TeleMedicine,  patient health education,
patient health education,  shared decision making ehealth
shared decision making ehealth Voice Health Summit Spotlight 2018
 October 23, 2018
October 23, 2018 During the Voice.Health Summit in Boston last week, innovators gathered to explore opportunities, discuss issues and to experience different voice technology use cases.
 BCH John Brownstein shares voice health use casesJohn Brownstein, Chief Innovation Officer at Boston Children’s Hospital is excited about the opportunity for healthcare to lead other verticals with this empowering technology which many of us use every day – Alexa tell me… Siri what is… ?
BCH John Brownstein shares voice health use casesJohn Brownstein, Chief Innovation Officer at Boston Children’s Hospital is excited about the opportunity for healthcare to lead other verticals with this empowering technology which many of us use every day – Alexa tell me… Siri what is… ?
Since the year 2000, the health technology industry has evolved from websites (e.g. patient portals) to mobile applications (mhealth) and now to voice and conversational assistants. There are many use cases which help patients and providers in different settings.
- In hospital, the doctor asks to see the patient’s latest lab results.
- Following a hospital discharge, the patient interacts with his virtual robot to record side effects from his new medications.
- Preparing for an outpatient visit, a patient verbally responds to the pre-visit questions to share with her doctor.
- Days after a remote monitoring visit, a patient asks additional questions to help her manage her asthma.
Although voice health technology is in the early adoption stage, health innovators are convinced that these virtual voice assistants can address real problems -- the shortage of healthcare professionals, clinician burn out, inefficiencies in patient care, lack of patient engagement and the inability to personally support patients along their health journey outside of the hospital. Nuance’s Peter Durlach stresses the importance of using these technologies to free up the clinicians to take care of patients.
Voice has many unique benefits for healthcare. Dr. Rupal Patel, CEO VocalID describes the convenience (e.g. hands free), the capability to capture information and insights about the user (e.g. gender, size, bio- markers) and ability to generate trust through continuous listening and personalized responses. Other benefits include the ability to capture context (e.g. surroundings, urgency and intent) and empower the user (e.g. patient feels a sense of control). Amazon’s Emily Roberts, Sr. Marketing Manager adds the value of capturing “moments of the day” by incorporating voice into other devices (e.g. smart home/refrigerator, car).
Voice Health in Action
During the Voice.Health Summit, we saw what “voice-first” can deliver in five different care setting exhibits. Here are some interesting examples of use cases to bring value to patients and/or the care team.
1. Hospital/Patient. With the Joint Commission’s focus on “accurate screening and assessment of pain”, Dr. Samir Tulebaev, Geriatrician and the Center of Nursing Excellence at Brigham and Women’s Hospital are working with Orbita’s CEO Nate Treloar on the development of a post- operative pain management voice assistant. The patient tells her bedside teddy bear Briggie (which has a built in microphone) that she is in pain, describes where the pain is and indicates if the pain is intolerable. Her nurse immediately receives a secure text message to respond.
2. Hospital/Clinical. Cedars-Sinai uses Sopris Assistant to record, summarize, approve and place the patient care note into the EHR. The AI summons the listening technology, drives the summary and produces the intelligent note for physicians. Cedars-Sinai helped Sopris Health create an experience and workflow catered to hospitalist.
3. Senior Living & Home Health. Caregivers can engage an aging patient with the AI powered LifePod virtual assistant which serves as a personalized companion, delivers reminders, and monitors daily activities. LifePod’s CEO Stuart Patterson emphasized the importance of “proactive voice” which shares and captures essential information without relying on the person to ask (i.e. reactive voice).
4. Consumer Home. Anne Weiler, CEO Wellpepper, the winner of the Alexa Diabetes Challenge, engages a patient who is recently diagnosed with type 2 Diabetes. She uses her voice to weigh herself, scan her feet for ulcers and track her care plan tasks. This voice assistant gives the patient an opportunity to proactively engage whenever she wants.
5. Vocal Biomarker Lab. Sonde Health is interested in capturing and using a patient’s voice samples as health measures for different physical (e.g. sinus congestion) and mental health conditions (e.g. depression, suicide risk).
Lessons from Voice Health Innovators
As with any new technology, there is a lot to learn from the pioneers.
Real Problem Definition: Sara Holoubek, CEO Luminary Labs emphasized the importance of deciding who (e.g. newly diagnosed) and what (e.g. help with self-management) as a first step to focus the development planning process.
Patient/User Input: Deloitte's Debbie Hays, Specialist Executive discussed the patient journey research for the DeloitteASSIST voice solution which revealed the “challenges and delays” that needed to be addressed while the patient is in the hospital room.
Patient/User Feedback: Karin Beckstrom, Sr. Product Manager ERT Innovation Lab (formally PHT) described using voice to capture patient reported outcomes (PROs) on a daily basis. We ask-- how engaging was it? Are you willing to answer questions on a daily basis? How difficult was the skill? Did Alexa understand you?
 "Flu Doctor" from Seattle Children's Hospital Stacey UlaciaPersonalization: Stacey Ulacia, Sr. Communications Specialist at Seattle Children’s Hospital in partnership with Boston Children’s Hospital, developed the “Flu Doctor” voice skill. This brings more value since it is customized based on the zip code provided by the patient.
"Flu Doctor" from Seattle Children's Hospital Stacey UlaciaPersonalization: Stacey Ulacia, Sr. Communications Specialist at Seattle Children’s Hospital in partnership with Boston Children’s Hospital, developed the “Flu Doctor” voice skill. This brings more value since it is customized based on the zip code provided by the patient.
Opportunities for Voice to Solve Healthcare Problems
There are many use cases for voice technology to help drive the triple aim.
UPMC’s Dr. Shivdev Rao believes it would be valuable to use voice to help triage a care situation, and capture information from the patient pre or post exam.
Boston Children’s Hospital Dr. Docktor shared Pediatrics Voice Hackathon examples including one which uses voice to help a patient prepare for his procedure at home with instructions and images that are tailored to his specific health issues (e.g. food problems).
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles is collaborating with Sumeet Bhalitia, Founder & CEO Avia to bring voice into the hospital room, giving the patient control over their experience and the ability to get assistance as needed (e.g. bathroom help) with the goal of increased patient satisfaction.
 Recent metrics for Answers by CignaCigna’s Laura Schuntermann, Global Head of Digital Strategy & Partnerships is excited by the growth of voice search. Gartner predicts by 2020, 30% of searches will be voice activated. Laura shared results from the voice solution Answers by Cigna which helps members get the information they need to make better health care decisions.
Recent metrics for Answers by CignaCigna’s Laura Schuntermann, Global Head of Digital Strategy & Partnerships is excited by the growth of voice search. Gartner predicts by 2020, 30% of searches will be voice activated. Laura shared results from the voice solution Answers by Cigna which helps members get the information they need to make better health care decisions.
Novartis’s Robert Stevens, Executive Director of Digital Strategy & Medical Innovation described voice health use cases that help clinicians determine the diagnosis/clinical decision support, check guidelines, send RXs to pharmacy and order follow up patient education.
Future Voice Health Considerations
Although there is excitement around voice health, innovators are working to remove speed bumps to accelerate adoption:
Addressing Privacy/Security. Several organizations are anxiously awaiting for HIPAA compliant voice devices. There is also a concern that the device is always listening, even without the “wake” word.
Educating Patients about Voice. A few presenters admitted that patients do not know what they can ask. This means that either they are not using all of the voice capabilities or the patient has an unexpected experience -- Alexa says …. Hmm I do not know that one.
 Mayo Clinic's Optimizing Voice Content Creating complete Patient Experiences. Mayo Clinic’s Jennifer Warner, Sr Editor Global Business Solutions explains that voice is additive and does not replace other consumer engagement methods. Therefore, it is important to provide an “omni-channel” experience to engage and support the patient through every touch point.
Mayo Clinic's Optimizing Voice Content Creating complete Patient Experiences. Mayo Clinic’s Jennifer Warner, Sr Editor Global Business Solutions explains that voice is additive and does not replace other consumer engagement methods. Therefore, it is important to provide an “omni-channel” experience to engage and support the patient through every touch point.
Collaborating on Care Design. Maia Ottenstein, Digital Experience Design at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (DICE/design group within the hospital) is working on the “smart patient concierge” which empowers the patient to access assistance and resources on demand.
It will take a community of patient and clinical stakeholders to define, design and deliver voice technologies that bring real value to the users. It is encouraging to see that these stakeholders are coming together in hospitals, accelerators and innovation hubs to bring these voice technologies to life.


